Manganese in Grapes is an essential trace mineral that is required for several physiological processes, including bone development, wound healing, and carbohydrate metabolism. [1]
It is found in several foods, grapes are an excellent source of manganese.
In this article, we will explore the benefits of manganese, the role of grapes in providing this mineral, and other sources of manganese.

Importance of Manganese for Body
Manganese is a mineral that is essential for normal functioning of the body.
It plays a vital role in enzyme reactions, protein synthesis, and immune function.

Manganese also acts as an antioxidant, protecting the body from damage caused by free radicals.
Health Benefits of Manganese
Manganese offers numerous health benefits. Some of the key benefits include.
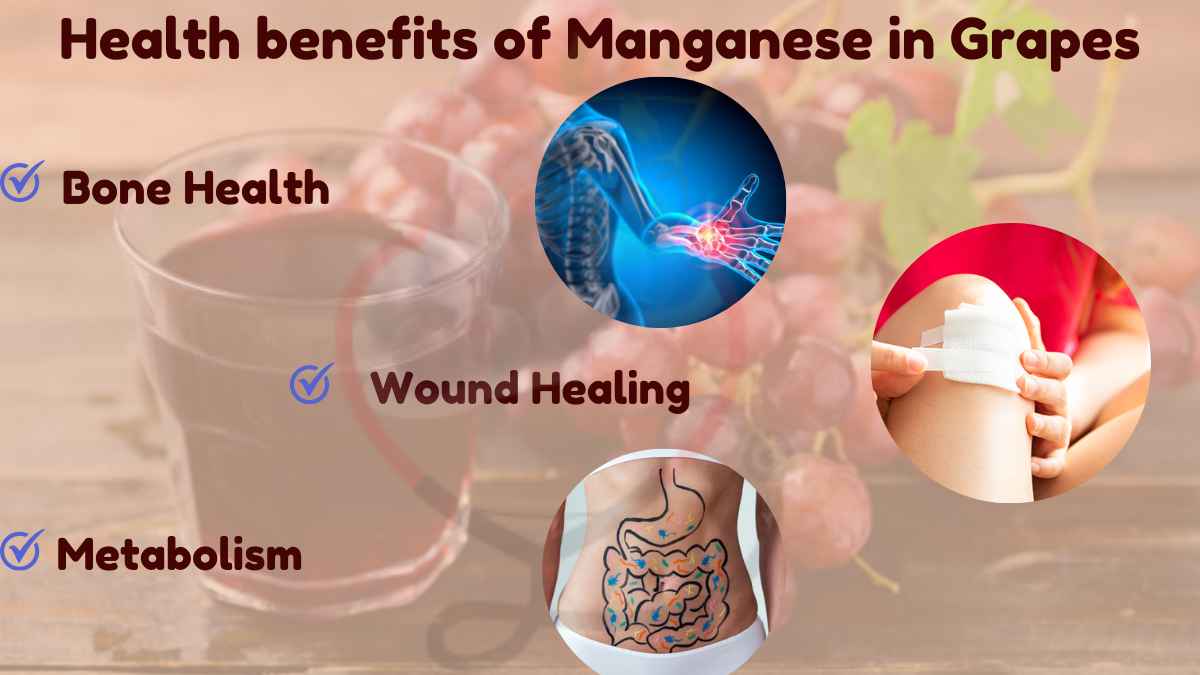
1: Bone Health
Manganese is essential for the development and maintenance of healthy bones. [2]
It helps in the production of collagen, a protein that provides structure to bones and other tissues.
2: Wound Healing
Manganese plays a critical role in wound healing. [3]
It helps in the formation of blood clots and the production of collagen, which is necessary for tissue repair.

3: Metabolism
Manganese is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, amino acids, and cholesterol. [4]
It helps in the conversion of food into energy and the regulation of blood sugar levels.
4: Antioxidant Properties
Manganese is a powerful antioxidant that helps in protecting the body from damage caused by free radicals. [5]
Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause cellular damage and lead to chronic diseases.
Amount of Manganese in Grapes
Grapes are an excellent source of manganese.
One cup of grapes contains approximately 0.07 mg of manganese.

Other Sources of Manganese
Apart from grapes, there are several other sources of manganese. Some of the key sources include:
1: Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are excellent sources of manganese. Almonds, pecans, and pumpkin seeds are particularly high in this mineral.
2: Whole Grains
Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and oatmeal, are also good sources of manganese.
3: Legumes
Legumes, such as chickpeas, lentils, and black beans, are rich in manganese.
4: Vegetables
Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and kale, as well as other vegetables, such as sweet potatoes and broccoli, are good sources of manganese.
Manganese is a vital mineral that offers numerous health benefits.
Grapes are an excellent source of this mineral, making them a healthy addition to your diet.
However, if you do not consume grapes, there are several other sources of manganese that you can include in your diet.
FAQs
How much manganese should I consume daily?
The recommended daily intake of manganese for adults is 2.3 mg for men and 1.8 mg for women.
Can consuming too much manganese be harmful?
Excessive intake of manganese can be harmful and lead to several health issues, such as neurological problems and muscle spasms. However, this is only a concern if you consume extremely high levels of manganese, which is rare.
Are there any side effects of consuming manganese?
Consuming moderate amounts of manganese is generally safe and does not cause any side effects. However, some individuals may experience minor symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Can I take manganese supplements?
Manganese supplements are available, but it is always best to get your nutrients from whole foods. If you are considering taking a manganese supplement, it is essential to talk to your doctor first.
Are there any foods that can reduce manganese absorption?
Some foods, such as tea and coffee, contain compounds that can reduce manganese absorption. It is best to consume these beverages in moderation and at different times than manganese-rich foods.